HBM117: Grave Oversight
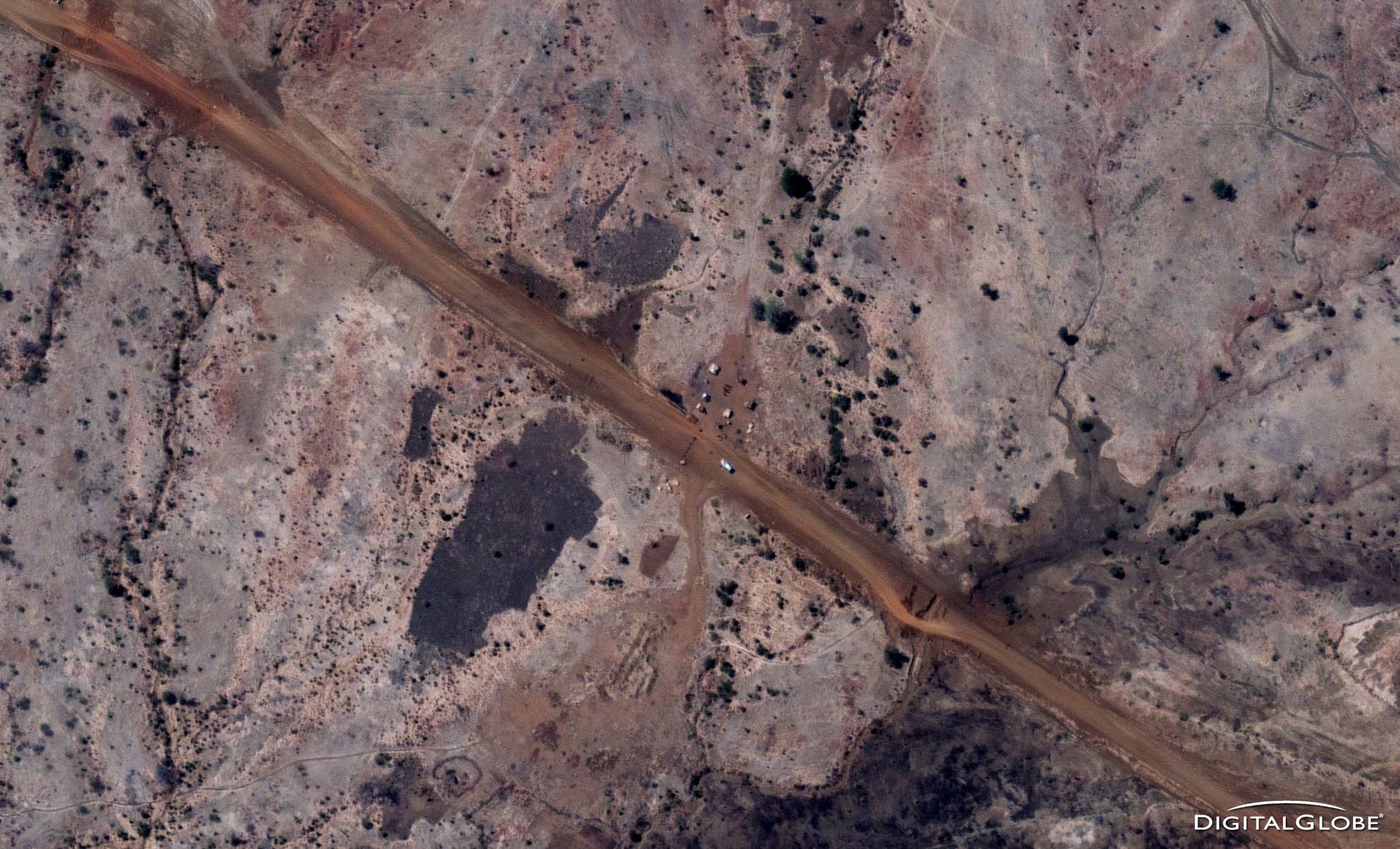
/Fire burning near Abyei town, composited with a shadow of a satellite for HBM by Jeff Emtman. Source image by DigitalGlobe
Sudan has been involved in ongoing civil wars since 1983. The wars were about religion, culture and resources. By 2005, approximately two million civilians had died. In 2011, the southern part of the country voted to secede from the north, creating the new country of South Sudan. But there were still three regions that were claimed by both north and south: Abyei, Blue Nile, and South Kordofan. These regions are rich in oil and have fertile farmlands, so politicians and humanitarians predicted there would be violence following the secession. Civilians in these regions, mostly farmers and shepherds, would be caught in the middle.
Content Note:
Discussion of genocide
Nathaniel Raymond is a human rights investigator. He was looking into an alleged massacre in Afghanistan when he was introduced to the idea of using satellite imagery for humanitarian purposes. At that time, satellite images were sometimes used for documenting force swells and finding the locations of mass graves. But Nathaniel wondered if he could figure out a way to use satellite imagery proactively; what if he could figure out a way to see an attack coming and sound an alarm before anyone got hurt?
Nathaniel wasn’t the only one who had this idea. Actor George Clooney had also been researching ways to use satellites as “anti-genocide paparazzi” in Sudan through an organization he co-founded called The Enough Project. The Enough Project and the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative and others sponsored the project. The Satellite Sentinel Project partnered with the private satellite imagery company DigitalGlobe, who gave the SSP permission to point some of their satellites where they pleased and take pictures. By December 2010, the Satellite Sentinel Project was in full swing, inventing a new methodology for analyzing satellite imagery of active conflict in real time.
The mission of the Satellite Sentinel Project was threefold:
Warn civilians of impending attacks,
document the destruction in order to corroborate witness testimony in later investigations, and
potentially dissuade the governments in both Sudan and South Sudan from returning to war in the first place.
“We wanted to see if being under surveillance would change the calculus… If they knew we were watching, would they not attack?” The Satellite Sentinel Project would release their reports at midnight so that they would be available in time for morning news in East Africa.
Critics of Satellite Sentinel Project say that South Sudan shouldn’t be a playground for experimental humanitarian efforts bankrolled by a foreign movie star. And Nathaniel says the critiques are valid. “It was always a Hail Mary pass. And, we must be clear, it was always an experiment, which in and of itself is problematic. But… what else are we going to do, sit on our hands?”
Satellite Sentinel Project released a total of 28 reports over 18 months. The methodology Nathaniel and his team developed is still being taught at the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative.
Today Nathaniel Raymond is a lecturer on Global Affairs at Yale’s Jackson Institute. Special thanks to Ziad al Achkar, one of Nathaniel’s colleagues from Satellite Sentinel Project that helped us with this episode.
Producer: Garrett Tiedemann
Editors: Bethany Denton and Jeff Emtman
Music: Garrett Tiedemann
Nathaniel Raymond, former Director of Operations at the Sentinel Satellite Project. Photo by Jeff Emtman.
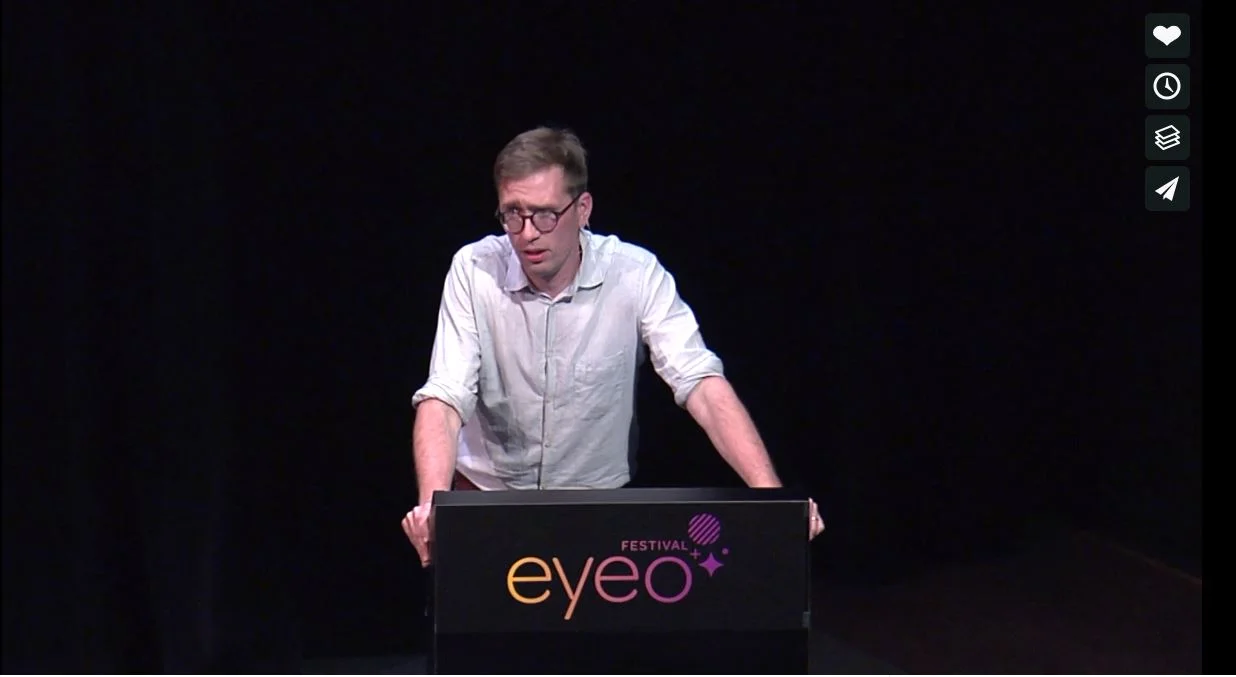
Nathaniel Raymond’s 2018 talk on Satellite Sentinel Project at the EyeO Festival 2018.
PBS Newshour Reporting on Satellite Sentinel Project’s documentation of burned villages in South Sudan.